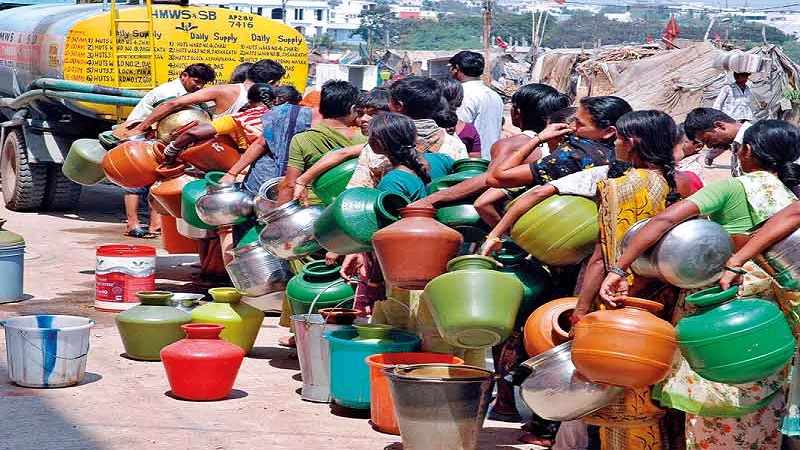
A slew of startups is set to change India’s water story in significant ways. They could create millions of jobs and renew urban and rural ecosystems while doing so. New inventions in water technology can propel India to a water rich nation from a water scarce nation. Startups and entrepreneurs can transform a negative narrative on water scarcity to a positive one within 5-10 years.
Experts predict that 21 cities in India will become dry in the next five years. Climate change and rapid depletion of ground water are exacerbating the water problem all over India. The Government of India created the Ministry of Jal Shakti to address these problems. However, their focus to date has been on macro level solutions such as river waters. This article focuses on micro level solutions by offering practical ideas for entrepreneurs. India can save about 50 plus billion gallons of water per day if all the below ideas are implemented. Ideas require zero sacrifice of existing water consumption for drinking, bathing, and other hygiene needs. The magic lies in how we use water and for what purpose. India’s water problem can be turned into a business opportunity in a massive way.
Waterless Washing
Several inventions are occurring in the field of waterless washing. The most promising technology is in the use of liquid CO2. At a very high temperature, CO2 becomes liquid and at a lower temperature it becomes gas. Therefore, a single machine can accomplish both the washing and the drying of clothes. Tersus Solutions in USA has accomplished this task. Its liquid CO2 washer cum dryer machine uses significantly less energy compared to a combination of a conventional water-based washer and a gas or electric dryer.
Solvair, USA, and LG, South Korea, have also made some advances in liquid CO2 washer cum dryer machines. Washing clothes with liquid CO2 enhances the life of fabrics, uses no detergent, micro plastics and dirt are not released into the water systems. Plus liquid CO2 is nontoxic, biodegradable, and fully recyclable.
A liquid CO2 laundromat with a drop-off and a pick-up type business serving every 50-100 households all over India could save about 10 billion gallons of water per day while providing employment for several million people. Today, most of the youth of India are underemployed. We have too many greeters, cashiers, bag checkers, waiters, etc., in stores and restaurants than required. Many women choose to be housewives due to lack of jobs. This human power could be more gainfully employed in a new laundromat industry that does not currently exist in India. The water saved for washing could now be diverted to water the trees on our highways that are starved for water. Plus, it allows us to grow more trees. Economic models should study the benefits of such water allocation and their impact on climate change.
There are other inventions in waterless washing. The startup, 80Wash, in Chandigarh uses its patented ISP steam technology – a low frequency radio-based microwave that uses very minimal water. The Whirlpool arm in India is also launching a low water-based washer. Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and other engineering colleges need to address the obvious and urgent problems facing India. Entrepreneurs need to more closely study liquid CO2 washers that are now in use by US Military. Entrepreneurs are providing liquid CO2 washing to hospitals and hotels in major cities such as Chicago, San Francisco, and New York City. The dense population of India allows for several million liquid CO2 laundromats to flourish and provide employment to millions and in the process the country becomes more water rich.
Liquid CO2 has many traditional applications whether it relates to refrigeration or cleaning of electronic or other industrial components. DyeCoo Textile Solutions in USA offers textile dyeing solutions with liquid CO2 that uses zero water and chemicals. Adoption of such technology will transform the entire textile industry of India and make it greener. India needs to invent liquid CO2 washing machines for restaurants. All utensils and silverware can be washed in a nontoxic and a safe manner. The wasted food residue can be composted and used as fertilizer instead of its release into the water systems – a new revenue stream for the restaurant industry.
The use of liquid CO2 is clean and green. It will save 10-15 billion gallons of water per day, saved water can grow new trees or invigorate existing water starved trees.
Innovative Materials to Recharge Groundwater
Startups and researchers are experimenting with permeable type materials that can recharge groundwater levels. If these highways and roads are covered with permeable type materials it would recharge our groundwater levels. Asphalt on roads and highways are non-permeable and exacerbate flood situations during heavy rainfall.
A company such as Tarmac in England makes a permeable type of concrete material called Topmix for roads, highways, and parking lots. It absorbs 880 gallons of water per minute. With climate change and flash floods the new normal, we need such novel permeable materials for our roads and highways to replenish our low groundwater levels. University researchers need to step up and meet this challenge.
Prevent Water Leaks
Several startups have created miniature marble sized robots with GPS technology that can detect water leaks in underground water pipes enabling municipalities to accurately dig and repair the pipes. This technology needs to be complemented with satellite technology that can narrow down the location of where the leaks are prevalent. Utilis Solutions, a company based in USA deploys such a type of satellite imaging technology that works well even in densely crowded areas.
Reduce Water Footprint
Several crops such as cotton, coffee, tea have a high water and a land footprint. If these products were made in the lab their water/land footprint will be low. The freed-up land could be used to grow more diverse species of trees. Such trees would attract more rain. Mono cropping with cash crops on precious hills contributes to deforestation and changes our weather patterns.
GALY in USA is already producing cotton in a lab, they use80 percent less land and water, and the cotton grown in the lab grows much faster than on land. Finland has successfully produced coffee in a lab, people in a blind study could not tell the difference between the lab grown coffee or the real coffee. Many startups are now geared to produce meat in the lab. The global water and land footprint of meat grown as food on land is significantly greater than all plant-based food. UN IPCC states that meat grown as food on land emits more greenhouse gases than all the vehicles in the world. Meat or coffee when grown in a lab are biologically like the land grown stuff. Lab grown meat can be titrated for lower fat content or be made hundred percent organic. As a policy, we must shift high resource utilizing items to the lab.
Fruit bearing trees attract rain, enrich the water table and the environment. Therefore, we should not produce such items in the lab. Interestingly, those which harm the environment seem to lend themselves to being produced in the lab, and those that are beneficial for the environment do not lend themselves to being produced in the lab. Fortunately, our creator has planned everything with perfect intelligence.
Better than Desalination
Dr. Praveen Kumar and his team at the University of Illinois, USA, have invented a process and a structure that harvests fresh water by absorbing the plentiful water vapor above the oceans. This technology is cheaper and superior to desalination and cloud seeding. The findings have been reported in Nature, a prestigious scientific journal. India can leapfrog and adopt such technologies.
https://www.inceptivemind.com/newly-proposed-method-harvests-untapped-sources-fresh-water/28962/
Interested entrepreneurs should check out the website, Imagine H2O, an organization that backs the best water entrepreneurs from concept to scale. They have supported 165 startups all over the world. They list interesting case studies on their site. Similarly, the WASH Innovation Hub in partnership with the Administrative Staff College of India, Telangana, supports innovative ideas with respect to water, sanitation, and hygiene. XPV Water Partners in Canada invests in a variety of water related companies across the world. They list their portfolio companies on their website. Entrepreneurs will greatly benefit by researching the business models of these companies.
Entrepreneurs need to study the business model developed by Madhukhar Swayambhu who deploys Vedic technologies to cure dead water bodies. His website, Vaidic Srijan describes the scientific methodology he uses. The wastewater treatment plant ECOSTP in Bengaluru uses zero energy and mimics the process of what happens in a cow’s stomach.
The Shafdan wastewater treatment facility in Israel treats and uses 95 percent of the wastewater for agriculture purposes. There are several startups tying up with wastewater treatment plants and turning waste into precious fertilizer using microbes. Modern Meadow in USA grows leather in a lab using microbes, therefore, they don’t pollute either the rivers or the groundwater unlike traditional leather tanning known for being one of the worst water polluters.
Opportunities in sustainable water innovations are enormous. Even simple innovations can make a big difference. For example, if a bath towel had a different color on each side, the consumer psychologically will use the towel for a longer time and may save more water. We can transform the bottled water industry by offering water in biodegradable plastic bottles.
Urgent action by Ministry of Jal Shakti, Universities, and entrepreneurs can transform India from a water scarce nation to a water rich nation. The water saved from all the above actions needs to be diverted to grow more trees and attract more rain. All listed actions have a multiplier effect to save water and mitigate the impact of climate change. The negative narrative of water scarcity can be transformed to a positive one. India needs to step up to this challenge.
In fact, growing of trees such as the peepul is known to repair the ozone layer through the release of an organic compound called isoprene. India needs to create greater awareness of the utility of the several sacred trees of India – our solution to climate change lies in our sacred trees, the wise use of our sacred water, soil, and animals. Leadership and entrepreneurship will be the enablers.
Ram Ramprasad worked as a Global Marketing Director for a Fortune 100 company in the USA. He authored two books and published articles in reputed magazines in India. He holds graduate degrees from Yale University, USA, and Madras University.